FAQs
Q- Am I required to have impact protection on my windows and doors?
A- Not necessarily, you will be required to have impact protection if you replace your windows and doors if you are in a windborne debris region. Most counties wont knock on your door and require you to make changes, but some counties like Miami dade can. Ask one of our consultants for details during your free in home consultation.
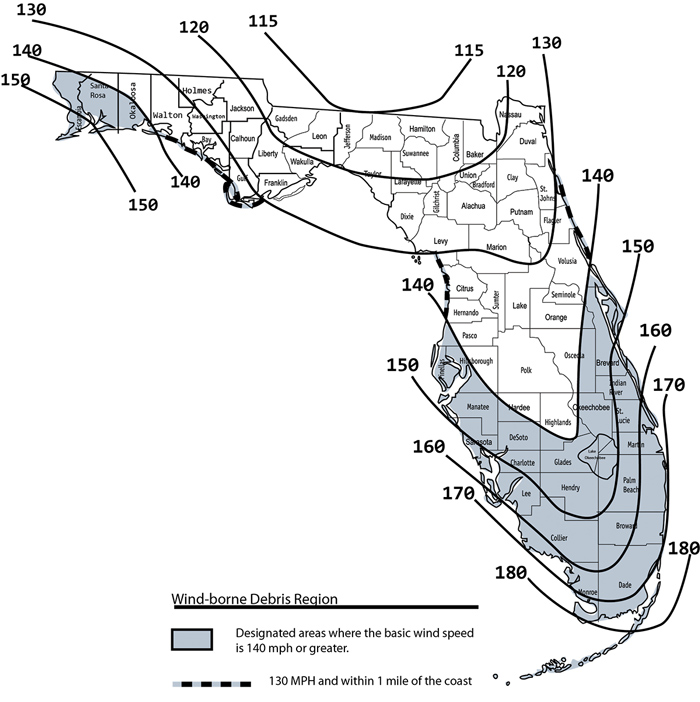
Q- Does my home fall in a windborne debris region?
A It might look at the map on this link to see if it does. If you're not sure you can check with your local building department or just call us we'll be happy to help.
Q- Do I have to have tinted glass?
A- Energy Star requirements have specific criteria which can by met by utilizing high tech glass options which may appear to have a slight tint.
GLOSSARY
AAMA: American Architectural Manufacturers Association. A national trade association that establishes voluntary standards for the window, door, storefront, curtain wall, and skylight industries.Argon gas: Argon is a safe, odorless, colorless, non-toxic, non-flammable inert gas that is commonly used in place of air between the glass panes of an insulated Low-E glass unit to reduce temperature transfer.
Balance: A mechanical device used in hung windows to offset the weight of the sash.
Balance shoe: Hardware that connects the balance to the sash.
Box screen: A heavy duty sliding glass door screen frame that simulates the actual glass panels. It is typically similar in size and shape to the glass door panels.
Corrosion-resistant: Refers to how well a substance can withstand damage caused by oxidization or other chemical reactions.
Cottage window: On a hung window the sash lite is larger than fixed lite.
Deglazing: An effect of severe weather on windows, where the silicone glazing bead separates from the window pane, thus reducing the window’s ability to restrict water from entering the structure and decreasing the strength of the overall window.
Design load: Wind load pressure, usually expressed in pounds per square foot (psf). Equal to 2/3 of the Structural Test Load.
Design pressure: See Design load.
Egress hinge: A hinge on the casement window that pivots closer to the corner and creates a greater clear opening.
Energy Star: ENERGY STAR® is an independent U.S. government program establishing a standard set of guidelines to recognize the energy efficiency of various products. ENERGY STAR® guidelines are used in conjunction with a variety of building materials, including windows and patio doors.
Florida Product Approval: A series of tests performed by a State of Florida approved testing lab to ensure certain building components meet Florida standards.
Forced-entry resistance: The test methods intended to establish a measure of resistance for window assemblies subjected to attacks, other than by impact.
Heat-strengthened glass: Glass that is reheated, after forming, to just below melting point, and then cooled, forming a compressed surface that increases its strength beyond that of typical annealed glass.
Impact resistant: Shatter-resistant glass, when the outer glass breaks the shattered pieces will adhere to an intermediate layer of a shatter-proof membrane.
Insulating glass: Window panes separated by an air or other gas filled space to reduce heat transfer.
Interlayer: A shatterproof membrane sandwiched between two panes of glass.
International Building Code: A model building code developed by the International Code Council that has been adopted throughout most of the United States.
Laminated Insulating glass: Comprised of three panes of glass: two panes bonded together with a strong, clear interlayer and one pane for added insulation.
Large Missile Impact: Test used on windows and doors in which a 9 lb 2x4 traveling at 50 ft per second is propelled at a speed of 34 mph into test subject.
Lift rail: A handhold for raising and lowering the sash. Rail implies that the handhold is continuous across the sash.
Lite: An area of visible light, framed by either a window or door’s primary extrusions or by muntins.
Low-E (Emissivity) glass: Glass with a transparent metallic oxide coating applied onto or into a glass surface. The coating typically allows short-wave energy to pass through but reflects long-wave infrared energy which improves the U-value.
Miami-Dade Notice of Acceptance: Protocol for testing windows for impact by large or small missiles.
Monolithic: Referred to as single unit of glass (not insulated).
Multiple chambered frame: Frame member which has multiple core construction to provide strength and insulation.
NFRC – National Fenestration Rating Council: A non-profit organization which provides energy performance ratings on windows, doors, skylights, and attachment products.
Obscure glass: Glass that has been made translucent instead of transparent. Pocket door: Sliding glass door that when opened slides clear of the opening. Prep: Used in reference to holes that get bored or punched on a door.
Sound Transmission Class (STC): The sound transmission loss rating of a material over a selected range of sound frequencies. The higher the number, the less sound is transmitted.
Super Spacer® nXtTM: An all-foam, warm edge spacer that lines the edge around the insulating glass panes. See page 14 for details about benefits.
Tempered glass: Treated glass that is strengthened by reheating it to just below the melting point and then suddenly cooling it. When shattered, it breaks into small pieces. Approximately four times stronger than standard annealed glass; is required as safety glazing in patio doors, entrance doors, side lights, and other hazardous locations. It cannot be recut after tempering.
Ultra-violet (UV): The invisible rays of the spectrum that are outside of the visible spectrum at its short-wavelength violet end. Ultraviolet rays are found in everyday sunlight and can cause fading of paint finishes, carpets, and fabrics.
Vinyl: A rigid or flexible material made of poly vinyl chloride material used in window and door frames and glazing.
Washable hinges: Track type hinges on casement windows that, aside from normal operation, have the ability to slide towards frame center and allow for easy sash cleaning.







